Indicator Gauge Icon Legend
Legend Colors
Red is bad, green is good, blue is not statistically different/neutral.
Compared to Distribution
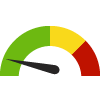 the value is in the best half of communities.
the value is in the best half of communities.
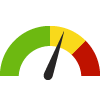 the value is in the 2nd worst quarter of communities.
the value is in the 2nd worst quarter of communities.
 the value is in the worst quarter of communities.
the value is in the worst quarter of communities.
Compared to Target
 meets target;
meets target;  does not meet target.
does not meet target.
Compared to a Single Value
 lower than the comparison value;
lower than the comparison value;
 higher than the comparison value;
higher than the comparison value;
 not statistically different from comparison value.
not statistically different from comparison value.
Trend

 non-significant change over time;
non-significant change over time; 
 significant change over time;
significant change over time;  no change over time.
no change over time.
Compared to Prior Value
 higher than the previous measurement period;
higher than the previous measurement period;
 lower than the previous measurement period;
lower than the previous measurement period;
 no statistically different change from previous measurement period.
no statistically different change from previous measurement period.
 Significantly better than the overall value
Significantly better than the overall value
 Significantly worse than the overall value
Significantly worse than the overall value
 No significant difference with the overall value
No significant difference with the overall value
 No data on significance available
No data on significance available
Chronic Hepatitis B Cases
This indicator is archived and is no longer being updated. Click to learn more
Why is this important?
Hepatitis B is a disease caused by a virus that attacks the liver. The virus, which is called hepatitis B virus (HBV), can cause lifelong infection, cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure, and death. Hepatitis B vaccine is available for all age groups to prevent HBV infection.
Surveillance data rates are only descriptive and causality cannot be inferred. Rates may be decreasing due to the implementation of immunization strategies to eliminate transmission of HBV in the U.S. These strategies include universal vaccination of infants at birth; immunoprophylaxis of infants born to hepatitis B surface antigen-positive women, or to women of unknown hepatitis B surface antigen status; routine vaccination of previously unvaccinated children and adolescents; and vaccination of previously unvaccinated adults at risk for HBV infection (e.g. heterosexuals with multiple sex partners, injection drug users, men who have sex with men, household contacts and sex partners of persons with chronic HBV infection). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), national rates of acute hepatitis B have decreased since 1990, but national estimates of chronic HBV infections range from 700,000 to 1.4 million, making it a public health concern.
State: Oregon
Measurement period: 2022
Maintained by: Conduent Healthy Communities Institute
Last update: September 2024
Graph Selections
Data Source
- Oregon Health Authority, Acute and Communicable Disease Program
Note: This source uses Zip Code Tabulation Areas (ZCTAs) for its Zip Code data. Learn more
Maintained By: Conduent Healthy Communities Institute (Methodology)
Filed under: Health / Immunizations & Infectious Diseases, Clinical Care